What is Selenium?
Selenium is an open-source framework for automating web browsers and testing web applications. It provides a way to interact with web pages programmatically using scripts, allowing for tasks such as filling out forms, clicking buttons, and asserting the presence of specific elements. It can be used for functional and regression testing of web applications across different platforms and browsers.
Why Selenium?
Selenium is used for automating web browser testing because it offers several benefits:
Cross-browser compatibility: Selenium supports a variety of browsers including Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Internet Explorer, making it possible to test a web application on multiple platforms.
Cost-effective: Selenium is open-source software and free to use, which can save significant costs compared to proprietary testing tools.
Easy integration: Selenium can be integrated with other tools and frameworks such as Java, Python, C#, and TestNG, making it easy to use for developers and testers with different technical backgrounds.
Large community: Selenium has a large and active community of users, which means that there is a wealth of knowledge, support, and resources available for users.
Flexibility: Selenium provides a range of APIs for different programming languages and platforms, allowing for customization and flexibility in the testing process.
What is XPath?
In Selenium, XPath is a powerful way to locate web elements in a web page's HTML structure. It is used in Selenium to find web elements such as buttons, links, text, tables, etc. based on their XML path. Selenium provides a method called "find_element_by_xpath" to locate elements using XPath. This method returns the first web element that matches the XPath expression provided. XPath expressions can be written to match a single element, multiple elements, or even all elements on a page. It provides a way to locate elements with high precision, even in complex HTML structures.
What is Maven?
Maven helps manage dependencies, builds, documentation, and reporting for projects. Maven provides a standard way of building projects, making it easier for developers to understand and work with the build process.
With Maven, developers can declare the dependencies needed for a project in a single file (pom.xml), and Maven will automatically download and manage those dependencies for them. This helps to ensure that the same version of a library is used consistently across different machines and development environments.
Setup Maven do Automation
Open IntelliJ IDEA and click on "Create New Project".
In the New Project window, select "Maven" under "Project SDK" and click on "Next".

In the next window, provide a GroupId, ArtifactId and a project location, and then click on "Next".
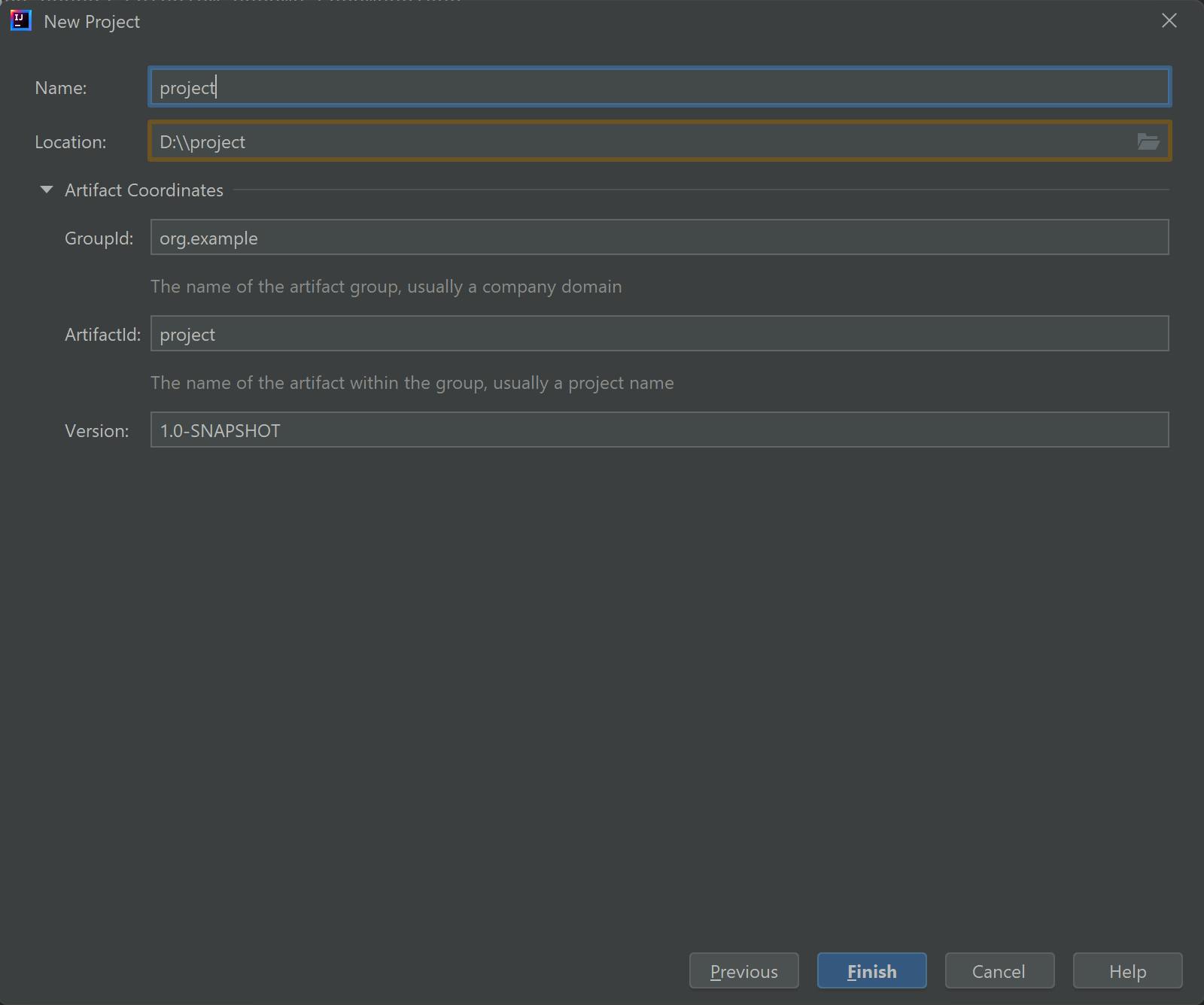
In the following window, leave the default options selected and click on "Next".
In the final window, click on "Finish".
In the Maven tab located in the right-hand side panel, right-click on the project and select "Add Framework Support".
In the "Add Framework Support" window, select "Java".
Add the following dependencies to the pom.xml file to include Selenium:
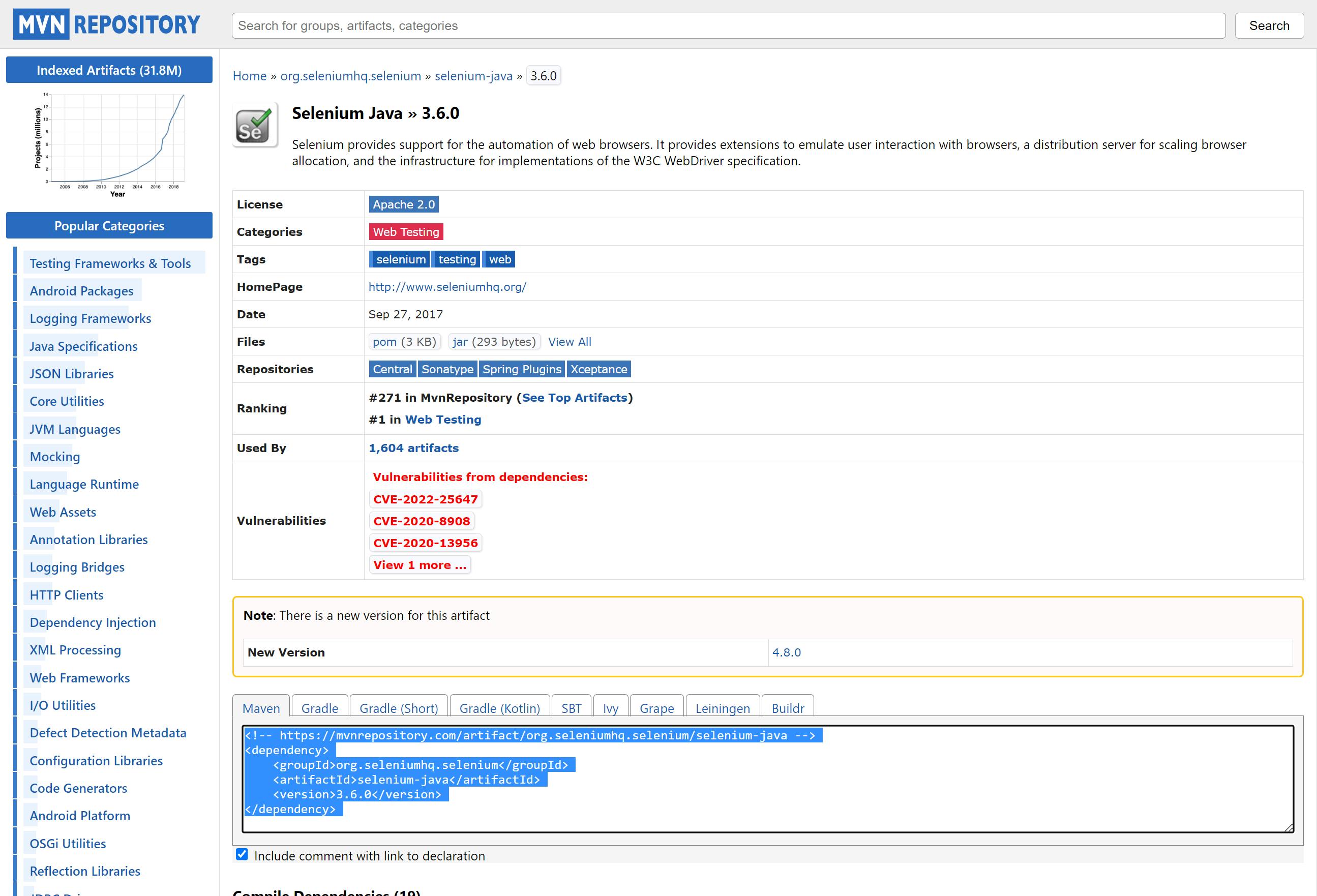
<dependencies><dependency> <groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId> <artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId> <version>4.0.0-alpha-6</version> </dependency></dependencies>Update the project by right-clicking on the project in the Maven panel and selecting "Reimport All Maven Projects".
Know your current web browser version
(ChromeDriver 109.0.5414.74)in the about section in the setting of the browser which you are using.Download the drivers according to your browser's version and save them to the resources folder in the project.

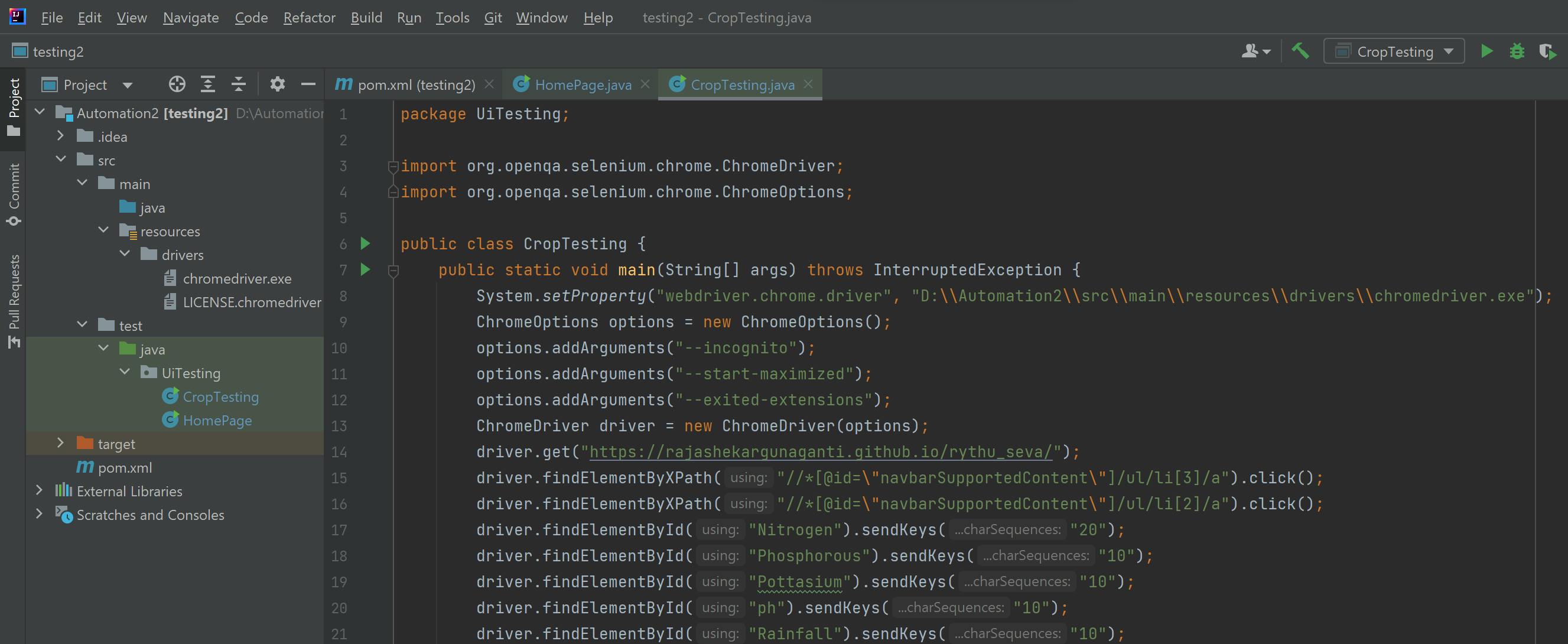
You can now start writing your Selenium tests in IntelliJ IDEA.
What now?
Start testing the user interface of a software application to verify its functionality, usability, and overall visual appearance. It involves checking for visual defects, validating the correct functioning of buttons, links, and other interactive elements, and ensuring the application meets the specified requirements and design standards.

